You are here
Understanding Genitourinary system
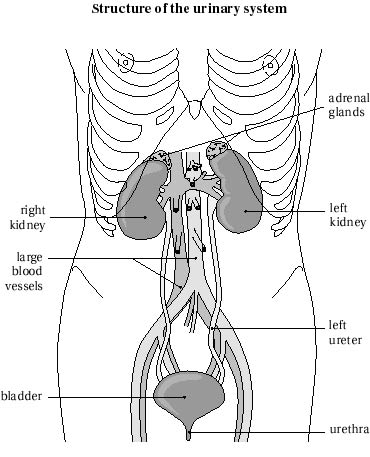
Kidney: Kidney also plays an important role in maintenance of blood pressure and blood hemoglobin values. A normal human being has two kidneys, one on each side of the body and these lie deep inside the belly over the back muscles.
Ureters: These are tubes which carry the urine produced in the kidney to the storage organ bladder. There is one ureter on either side and the normal ureter in a child is less than half a cm in diameter.
Urinary bladder: It is a specialized organ for storing urine till a convenient time and place are available for passing urine. The muscle of bladder is called Detrusor and it serves a very important function of maintaining low pressures even with increasing amount of urine inside it. This function is called bladder compliance and is very important in keeping us clean. Bladder has an excellent nerve supply whereby we can sense that it is full or empty.
Urethra: Urethra is a tubular organ which carries urine form bladder to outside- through the penis in males and to the vulva in females. Male urethra is longer and has a few bends, while female urethra is very short and straight. Male urethra has parts- posterior urethra which lies within the prostate gland and anterior urethra which lies within the penis. Posterior urethra receives ejaculatory ducts (vide infra).
Testes: Testes (singular testis) are paired organs which lie in the scrotum between legs. They serve two important functions- production of sperms and production of male hormones. When the baby is developing in mother's tummy, the testes lie within the belly of the baby. They gradually descend and pass through the abdominal wall to reach the final location in 8th month of pregnancy. If this does not happen- a condition called undescended testis results.
Scrotum: These are bags of skin which house the testis. They serve an important function of keeping the temperature of the testis lower (about 2 ºC) than the rest of the body.
Penis: Penis a specialized reproductive organ which serves as a conduit for urine as well for semen. It is rich in Vascularised tissue which can become engorged and assist in reproduction. The topmost part of penis is called Glans Penis, I children upto a certain age it is covered by foreskin or prepuce. As the child grows this separates from the glans and becomes retractable.
Epididymus: The sperms produced inside the testis mature in a cluster of tubules called Epididymus which lies within the scrotum hugging the lower part of testis.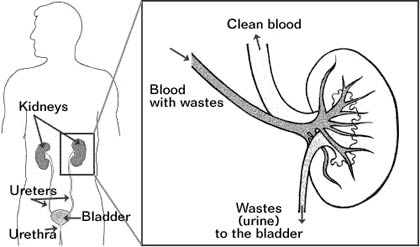
Vas deferans: This is very fine tube which carries sperms from epididymus to the posterior urethra through the prostate gland. These receive secretions from a specialized reproductive gland called seminal vesicles and are called ejaculatory ducts where they join posterior urethra (vide supra).